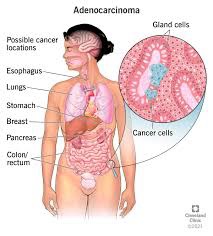
Uncategorized
Understanding the Impact of Cancer in the United States: Challenges, Progress, and Hope

Introduction:
Cancer remains one of the most pressing health challenges in the United States, affecting millions of lives each year. Despite significant advancements in research, diagnosis, and treatment, the burden of cancer continues to be felt across the nation. This article aims to explore the current landscape of cancer in the United States, including key statistics, challenges, recent developments, and avenues for progress.
Overview of Cancer Incidence and Mortality:
Cancer is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and the United States is no exception. According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), an estimated 1.9 million new cancer cases will be diagnosed in 2024, with approximately 609,000 cancer-related deaths expected to occur. These statistics underscore the significant toll that cancer takes on individuals, families, and communities nationwide.
Common Types of Cancer:
Various types of cancer affect Americans, with some being more prevalent than others. Among the most common types of cancer diagnosed in the United States are breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, and skin cancer. Each type presents its own set of challenges in terms of prevention, early detection, and treatment.
Risk Factors and Prevention:
While certain risk factors for cancer, such as age and genetics, cannot be modified, many lifestyle factors contribute to cancer development and can be modified to reduce risk. Tobacco use, poor diet, lack of physical activity, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to environmental carcinogens are among the primary modifiable risk factors. Public health efforts aimed at promoting healthy behaviors and implementing policies to reduce exposure to carcinogens play a crucial role in cancer prevention.
Screening and Early Detection:
Early detection is key to improving cancer outcomes, as it allows for timely intervention and treatment. Screening tests such as mammograms, Pap smears, colonoscopies, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests can help detect cancer at an early stage when it is most treatable. However, disparities in access to screening and healthcare services contribute to unequal outcomes among various demographic groups, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to address healthcare disparities.
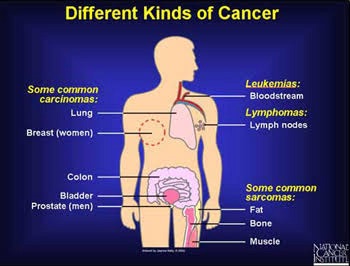
Advancements in Treatment:
In recent years, significant progress has been made in the development of new cancer treatments, including targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and precision medicine. These innovative approaches offer new hope for patients with advanced or treatment-resistant cancers, improving survival rates and quality of life. Additionally, advances in supportive care and symptom management have enhanced the overall cancer treatment experience for patients.
Challenges in Cancer Care:
Despite advancements in cancer research and treatment, several challenges persist in the delivery of cancer care. Access to high-quality cancer care remains a concern, particularly for underserved populations and rural communities. Additionally, the rising cost of cancer treatment poses financial burdens for patients and healthcare systems alike. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes equity, affordability, and innovation in cancer care delivery.
The Role of Research:
Research plays a central role in driving progress against cancer, from basic science discoveries to clinical trials and implementation science. Government agencies, academic institutions, nonprofit organizations, and pharmaceutical companies collaborate to fund and conduct research aimed at advancing our understanding of cancer biology, improving treatment options, and enhancing cancer prevention and control efforts.
Community Engagement and Advocacy:
Community engagement and advocacy are essential components of the fight against cancer, empowering individuals and communities to take action and drive positive change. Cancer survivors, caregivers, healthcare providers, researchers, and advocates work together to raise awareness, promote early detection, support policy initiatives, and mobilize resources to improve cancer outcomes and quality of life for all those affected by the disease.
Conclusion:
Cancer remains a formidable challenge in the United States, but significant progress has been made in understanding, preventing, and treating the disease. By addressing key risk factors, expanding access to screening and treatment, fostering innovation in cancer care, and promoting equity and advocacy, we can continue to make strides in reducing the burden of cancer and improving outcomes for individuals and communities across the nation. Together, we can work towards a future where cancer is no longer a leading cause of suffering and loss, but a manageable and preventable disease.